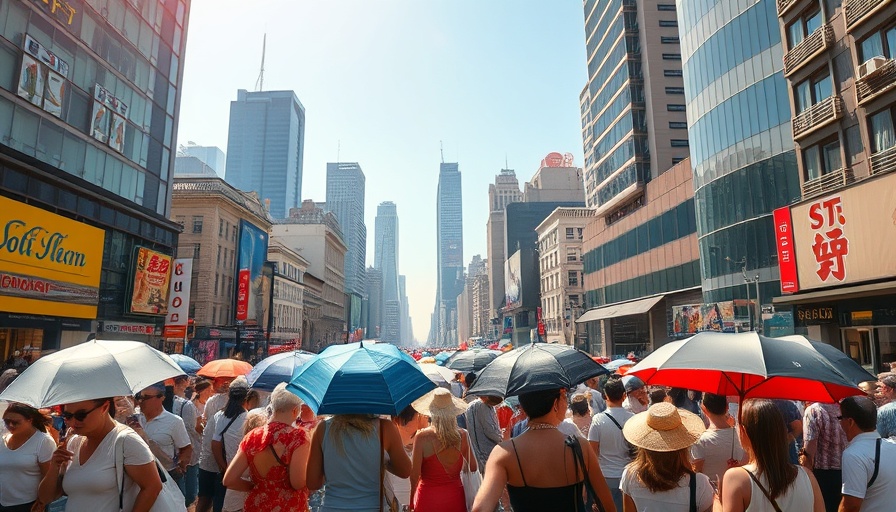

India's Battle Against Rising Heat: A Short-Term Lens
As India's scorching summers become increasingly severe, the urgency to develop effective Heat Action Plans (HAPs) is rising. While local governments recognize the threat of extreme heat, they seem trapped in a cycle of short-term solutions. Last summer was particularly revealing, as an unprecedented heatwave struck early in February, followed by an unsettling continuation of above-normal temperatures throughout the spring months. With more than 76% of the population exposed to high risk from extreme heat, experts are alarmed at the lack of systemic change in responses to this pressing issue.
Re-thinking Heat Action Plans: A Need for Holistic Solutions
Initially launched in 2013, India's HAPs aimed to safeguard public health and manage food security, but recent studies indicate numerous gaps. While over 250 cities have constructed their HAPs in reaction to the government's encouragement, a substantial majority of these plans remain woefully underfunded and poorly coordinated. A report from the Sustainable Futures Collaborative (SFC) reveals that from 2018 to 2023, surveyed cities implemented around 150 heat-related measures. Most of these adjustments were reactive, such as setting up temporary water stations or altering school schedules during heatwaves, with insufficient attention toward long-term climate resilience.
The Need for Resilient Urban Planning
Long-term infrastructure changes that would significantly enhance climate resilience, like climate-sensitive housing, have been largely neglected. As a result, most initiatives remain concentrated on immediate healthcare responses, often at the expense of more transformative actions. “No imagination of what long-term climate resilience looks like” is a reflection of the current mindset, according to SFC co-author Aditya Valiathan Pillai. In this atmosphere, historically, areas with significant heat risks, often the most impoverished, are sidelined in these discussions, receiving none of the potential cooling projects like tree-planting or water-body restoration, purely due to existing land ownership frameworks and urban infrastructure challenges.
Engaging Communities and Sourcing Sustainable Solutions
Effective HAPs must transcend common perceptions of heat solely as a health issue. They must integrate challenges related to labor rights, housing, and urban planning. Greenpeace India's Selomi Garnaik emphasizes that many action plans lack meaningful investments, with decisions often made top-down without adequate community input, diminishing their relevance. This perspective points to the need for community-centric approaches that harness the active participation of urban residents in decision-making processes, thus ensuring the plans reflect local needs and realities.
A Path Forward: Sustainable, Community-Driven Projects
In confronting climate change and extreme heat, a broadened focus that incorporates concepts of sustainability and ecological stewardship becomes paramount. As cities face planting real solutions—from developing community gardens to implementing green infrastructure—engaging the population in sustainable practices increases the chances of effective climate adaptation. Such community engagement paves the way for initiatives that not only respond to but also preempt the worsening impacts of climate change.
Taking Action: Why Your Voice Matters
Understanding the intricacies of India's HAPs is more vital than ever as climate change continues to deepen its grip. Individuals can contribute to a more sustainable future by advocating for more sustainable projects in their communities, investing in eco-friendly products, and promoting awareness around climate resilience. The call to action is clear: as a society, we must push for plans that prioritize long-term solutions over short-term fixes to protect vulnerable populations and enhance urban resilience.
Reflecting on the failures of existing heat action plans can galvanize citizens and policymakers alike, allowing for the integration of innovative solutions centered on community, sustainability, and ecological impact. These collaborative efforts can ultimately foster a climate-conscious society prepared for the heat waves of tomorrow.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


Write A Comment